Soil!
Soil is the part of the regolith that supports the growth of plants
Major Components of Soil
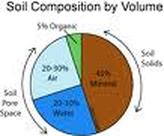
*Soil Compesition
The four major components of soil are mineral matter(broken down rock); organic matter or humus, which is decayed remains of organisms;water; and air. The proportions of these components differ in the different types of soil. The organic matter in soil consists of decayed remains of plant and animal life. The other half has pour spaces where air and water circulate.
The four major components of soil are mineral matter(broken down rock); organic matter or humus, which is decayed remains of organisms;water; and air. The proportions of these components differ in the different types of soil. The organic matter in soil consists of decayed remains of plant and animal life. The other half has pour spaces where air and water circulate.
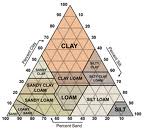
*Soil Texture and Structure
Soil texture refers to proportions of different partical sizes.Texture affects the ability to support plant life. Loam soil can retain water better and store more nutrients than soils composed mostly of clay or sand. This makes loam soil better for plant growth. Soil structure determines how easily a soil can be cultivated to erosion It also affects the way water can penetrate soil.
Soil texture refers to proportions of different partical sizes.Texture affects the ability to support plant life. Loam soil can retain water better and store more nutrients than soils composed mostly of clay or sand. This makes loam soil better for plant growth. Soil structure determines how easily a soil can be cultivated to erosion It also affects the way water can penetrate soil.
Click here to edit.
*Soil Formation
* The most important soil formation are parent material, time, climate, organisms, and slope.
* Soil contains of weathered rock and the remains of living things.
* Soil is formed by weathered rocks
**Parent Material effects the rate of weathering and the rate of soil formation
* The chemical makeupof the parent material affects the soils material
*Mechanical weathering produces soil that is like the parent rock
*Chemical weathering produces soil that is different from the parent rock
Time-The longer it takes the soil to form, the thicker it gets. As weathering continues the influence of the parent material can be overshadowed by the other factors
Climate-Differences if temperature and precipitation influence the rate,depth, and type of weathering. Climate also has a big effect on organisms that live in the soil
Organisms-Based on type and the number of organsims, they can have a major impact on is physical and chemical properties.Plants,animals, or microorganisms are the main source of organic material in soil. Microoragnisms also play a big part indecomposing things
Slope-Because the slope of land varies, the soil types may differ.On steep slopes erosion is accelerated. Soils are usually thin due to the little amount of water that can soak into the land.The direction of slopes also affets soil formation. Ex: soils on south-facing slopes are usually warmer and drier.
* The most important soil formation are parent material, time, climate, organisms, and slope.
* Soil contains of weathered rock and the remains of living things.
* Soil is formed by weathered rocks
**Parent Material effects the rate of weathering and the rate of soil formation
* The chemical makeupof the parent material affects the soils material
*Mechanical weathering produces soil that is like the parent rock
*Chemical weathering produces soil that is different from the parent rock
Time-The longer it takes the soil to form, the thicker it gets. As weathering continues the influence of the parent material can be overshadowed by the other factors
Climate-Differences if temperature and precipitation influence the rate,depth, and type of weathering. Climate also has a big effect on organisms that live in the soil
Organisms-Based on type and the number of organsims, they can have a major impact on is physical and chemical properties.Plants,animals, or microorganisms are the main source of organic material in soil. Microoragnisms also play a big part indecomposing things
Slope-Because the slope of land varies, the soil types may differ.On steep slopes erosion is accelerated. Soils are usually thin due to the little amount of water that can soak into the land.The direction of slopes also affets soil formation. Ex: soils on south-facing slopes are usually warmer and drier.
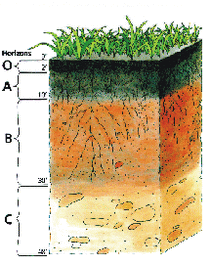
*Soil Profile
Soil profile is the vertical section through all the soil horizons.
Horizons seperarate all of the soil layers.
A Horizon
A horizon is known as topsoil or the uppermost layer of soil. The upper part contains mainly organic matter. The lower part is a mixture of mineral matter and organic matter.
B Horizon
The B horizon is known as subsoil.It contains clay and some humus. Sometimes the clay will compact, which is known as the impenetrable layer called hardpan.
C Horizon
The C Horizon consists of partly weathered rock. The composition is similar to the parent rock.
The development of these hprizons depend on time, climate, the type of rock, and surface features of the reign.
Soil profile is the vertical section through all the soil horizons.
Horizons seperarate all of the soil layers.
A Horizon
A horizon is known as topsoil or the uppermost layer of soil. The upper part contains mainly organic matter. The lower part is a mixture of mineral matter and organic matter.
B Horizon
The B horizon is known as subsoil.It contains clay and some humus. Sometimes the clay will compact, which is known as the impenetrable layer called hardpan.
C Horizon
The C Horizon consists of partly weathered rock. The composition is similar to the parent rock.
The development of these hprizons depend on time, climate, the type of rock, and surface features of the reign.
Title.
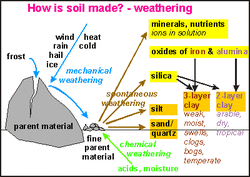
Weathering Processes
Weathering is the change in the physical form or chemical composition of rock material exposed to the earths surface.
There are two types of weathering:
Physical Weathering- processes which physically breaks rok into smaller pieces but does not change the chemical composition
Chemical Weathering- processes which break down rock by changing the chemical composition
*Types of Physical Weathering
Frost Wedging- this happens when water gets into the cracks of rock and freezes, which creases pressure on the rock. If this cycle continues the rock will eventually break apart.
Weathering is the change in the physical form or chemical composition of rock material exposed to the earths surface.
There are two types of weathering:
Physical Weathering- processes which physically breaks rok into smaller pieces but does not change the chemical composition
Chemical Weathering- processes which break down rock by changing the chemical composition
*Types of Physical Weathering
Frost Wedging- this happens when water gets into the cracks of rock and freezes, which creases pressure on the rock. If this cycle continues the rock will eventually break apart.
