Mountain Building
Factors Effecting Rock Deformation
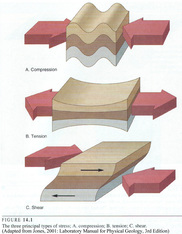
Deformation-is the general term for the processes folding,Shearing,faulting,compression or extension of rocks as the result of various natural forces
Stress-is the force per unit area acting on an object
Strain-is the change in shape or volume of a body of a rock as a result of stress
Things that determines the strength of a Rock
Temperture,Confining Pressure,Time,and Rock Type
Stresses that Effect Rocks
Compression-When rocks are squeezed or shortened
Tension-When rocks are pulled in opposite directions
Shear-when a body of an rock is being distorted
Types of folds
Anticline-is a fold in a sedimentary strata resembling an arch
Synclines-is a linear downfold in sedimentary strata
Monoclines- is a large steplike fold in otherwise horizontal sedimentary strata
Types of Faults
Normal Fault-is a fault in which the rock above the fault plane has moved down relative to the rock below
Reverse Fault- is a fault in which the material above the fault plane moves up in relation to the material below
Thrust fault-is a reverse fault with a dip less than 45 degrees normally about 10-15 degrees
Strike-slip Fault-a fault along which the movement is horizontal and parallel to the trend of the fault
Stress-is the force per unit area acting on an object
Strain-is the change in shape or volume of a body of a rock as a result of stress
Things that determines the strength of a Rock
Temperture,Confining Pressure,Time,and Rock Type
Stresses that Effect Rocks
Compression-When rocks are squeezed or shortened
Tension-When rocks are pulled in opposite directions
Shear-when a body of an rock is being distorted
Types of folds
Anticline-is a fold in a sedimentary strata resembling an arch
Synclines-is a linear downfold in sedimentary strata
Monoclines- is a large steplike fold in otherwise horizontal sedimentary strata
Types of Faults
Normal Fault-is a fault in which the rock above the fault plane has moved down relative to the rock below
Reverse Fault- is a fault in which the material above the fault plane moves up in relation to the material below
Thrust fault-is a reverse fault with a dip less than 45 degrees normally about 10-15 degrees
Strike-slip Fault-a fault along which the movement is horizontal and parallel to the trend of the fault
Types of Mountains

Mountains are classified by the dominant processes that have formed them.
The collection of processes that produce a mountain belt is called orgenesis.Orgenesis is the processes that collectively result in the formaton of mountains.
Mountains that are formed mostly by folding is called folded mountains.Folded Mountains are mountains that were mostly created by compressional stresses that make folds in rock layers.
Large-scaled normal faults are associated with structures called Fault-block mountains.Fault-block mountains are formed when to large blocks of are tilted,uplifted,or dropped between large normal faults.
As the crust is being streched a block called a graben that is bounded by normal faults drops down.
Graben is a valley formed by the downward displacement of a fault-bonded Block.
Grabens produce a long valley bordered by relatively uplifted structures called horsts.
Horsts are a elongated uplifted block of crust bounded by faults.
Uplifted Mountains are domes and basins.
Domes are formed when upwarping produces a circular or elongated structure.
Basins are downwarped structures having a circular shape.
The collection of processes that produce a mountain belt is called orgenesis.Orgenesis is the processes that collectively result in the formaton of mountains.
Mountains that are formed mostly by folding is called folded mountains.Folded Mountains are mountains that were mostly created by compressional stresses that make folds in rock layers.
Large-scaled normal faults are associated with structures called Fault-block mountains.Fault-block mountains are formed when to large blocks of are tilted,uplifted,or dropped between large normal faults.
As the crust is being streched a block called a graben that is bounded by normal faults drops down.
Graben is a valley formed by the downward displacement of a fault-bonded Block.
Grabens produce a long valley bordered by relatively uplifted structures called horsts.
Horsts are a elongated uplifted block of crust bounded by faults.
Uplifted Mountains are domes and basins.
Domes are formed when upwarping produces a circular or elongated structure.
Basins are downwarped structures having a circular shape.
Mountain Formation
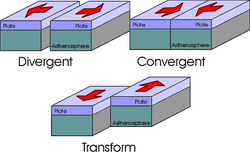
Convergent
Most mountains are formed by convergent plate boundaries.
Ocean-Ocean Convergence
Occurs where two oceanic plates converge and one is subducted beneath the other.Mainly produces volcanic mountains.
Ocean-Continental Convergence
Is the convergence of an oceanic plate and a plate whose leading edge contains continental crust. Mountains formed by ocean-continental convergence are volcanic mountains and folded mountains.
Continent-Continent Convergence
At a convergent boundary between two plates carrying continental crust, a collision between the continental fragments will result and form folded mountains.
Divergent
Mountains that are formed along ocean ridges at divergent plate boundaries are fault-block type mountains.
Transform
Two plates grinding past each other does not slide in a very smooth matter.
Isostatic adjustment
Isostasy-the concept that Earth’s crust is floating in gravitational balance upon the material of the mantle.Process of establishing a new level of gravitational equilibrium.Because of isostasy, deformed and thickened crust will regionaly uplift during mountain building and for a long period afterward.
Most mountains are formed by convergent plate boundaries.
Ocean-Ocean Convergence
Occurs where two oceanic plates converge and one is subducted beneath the other.Mainly produces volcanic mountains.
Ocean-Continental Convergence
Is the convergence of an oceanic plate and a plate whose leading edge contains continental crust. Mountains formed by ocean-continental convergence are volcanic mountains and folded mountains.
Continent-Continent Convergence
At a convergent boundary between two plates carrying continental crust, a collision between the continental fragments will result and form folded mountains.
Divergent
Mountains that are formed along ocean ridges at divergent plate boundaries are fault-block type mountains.
Transform
Two plates grinding past each other does not slide in a very smooth matter.
Isostatic adjustment
Isostasy-the concept that Earth’s crust is floating in gravitational balance upon the material of the mantle.Process of establishing a new level of gravitational equilibrium.Because of isostasy, deformed and thickened crust will regionaly uplift during mountain building and for a long period afterward.
